How Does Valley's Qualification and Scoring System Work?
Table of contents
Try Valley
Make LinkedIn your Greatest Revenue Channel ↓

Saniya Sood
How Does Valley Score Prospects for ICP Fit?
Valley's ICP scoring system combines textual analysis with deep research to evaluate every prospect against your defined criteria. Unlike form-based scoring that relies on rigid checkboxes, Valley uses natural language processing to understand nuanced qualification criteria. You define your ICP in plain language, and Valley's AI interprets and applies these criteria intelligently.
The scoring process examines multiple dimensions: individual factors (title, seniority, experience, skills), company factors (size, industry, growth stage, technology stack), behavioral signals (LinkedIn activity, content engagement, job changes), and contextual indicators (recent funding, hiring patterns, strategic initiatives). Valley synthesizes these into two scores: ICP fit (how well they match your criteria) and overall prospect score (likelihood to engage and convert).

The beauty of Valley's approach is its flexibility. You might specify: "We want VPs of Sales at Series B SaaS companies with 50-200 employees, who are hiring SDRs and have recently raised funding." Valley interprets this holistically, recognizing that a VP of Revenue at a Series A company growing rapidly might be equally qualified.
This intelligent interpretation prevents rigid scoring from excluding good prospects.
► Book a demo and explore how Valley can support your use case.
What Research Does Valley Conduct for Qualification?
Valley's qualification research spans 100+ data points from diverse sources, far exceeding what traditional scoring tools access. The platform examines: LinkedIn profiles and activity history, entire company websites (every page indexed), job postings and hiring patterns, funding history and investor information, technology stack from various signals, news mentions and press releases, social media presence and engagement, and podcast/speaking appearances.
This research depth enables sophisticated qualification. For example, Valley can identify companies using specific technologies like Workiva or Oracle EPM through job postings mentioning required experience. It can detect growth signals through hiring velocity, expansion announcements, or office openings. It can even identify cultural fit through content analysis and communication style.
The research is automated but intelligent. Valley doesn't just collect data - it interprets relevance. If your ICP prioritizes companies with recent funding, Valley weighs funding announcements heavily. If you care about technical sophistication, it emphasizes technology stack signals. This contextual interpretation ensures qualification matches your actual priorities, not generic scoring rules.
► Check Valley's Incredible Outreach: A compilation of real time messages and responses!
How Accurate Is Valley's "Delete Low ICP Fits" Feature?
Valley's low ICP fit detection achieves remarkable accuracy when properly configured. Users consistently report trusting the system completely: "Valley tends to be very good at scoring prospects. I tend to trust the low ICP fit button and haven't run into any situations where I missed anything."
The key to accuracy is thoughtful ICP definition. Valley performs best when given specific, measurable criteria rather than vague descriptions. Instead of "companies that would benefit from our solution," specify "B2B SaaS companies with 20-50 sales reps, using Salesforce, with average deal sizes above $10K." The more precise your criteria, the more accurate Valley's scoring.
The system handles edge cases intelligently. If someone from a generally low-fit company shows high engagement signals (viewing your profile, engaging with relevant content), Valley might score them medium rather than low, allowing for human judgment. This nuanced approach prevents mechanical exclusion of potentially valuable prospects while maintaining efficiency.
Can Valley Identify Buying Signals and Intent?
While Valley doesn't offer traditional intent data like Bombora or 6sense, it excels at identifying behavioral buying signals through its research and monitoring capabilities. Valley can detect: recent leadership changes (new executives often bring new initiatives), funding events (fresh capital means budget for new tools), rapid hiring (growth creates tool needs), technology changes (job postings revealing stack updates), and strategic initiatives (press releases about digital transformation).
Valley's warm prospect features amplify intent detection. Profile viewers demonstrate active interest by checking your profile. Post engagers show topical interest through content interaction. Company followers indicate organizational awareness. These behavioral signals, combined with deep research, create a powerful intent identification system.
Users can configure campaigns to prioritize intent signals. For example: "Target product managers who've engaged with posts about PLG strategies in the last 30 days" or "Focus on companies hiring for roles that mention our competitor's products." This dynamic targeting ensures outreach coincides with genuine buying interest.
How Does Valley Qualify Prospects from Different Sources?
Valley applies consistent qualification standards regardless of prospect source, ensuring uniform quality across all campaigns. Whether prospects come from Sales Navigator searches, LinkedIn post engagement, CSV uploads, or profile viewers, each receives the same deep research and scoring process.
The qualification process adapts to source-specific contexts. Post engagers get scored based on their engagement topic relevance plus standard ICP criteria. Profile viewers receive boosted scores for demonstrating interest. CSV uploads might include pre-qualification data that Valley validates and enriches. Sales Navigator searches get filtered based on search criteria plus Valley's deeper qualification.
This consistency ensures predictable quality. An agency owner explained: "Whether I'm uploading a client's list or scraping my competitor's post engagement, I know Valley will apply the same rigorous qualification. The 'Delete Low ICP Fits' button works the same way every time."
What Happens to Prospects Scored as Medium Fit?
Valley's three-tier scoring (High, Medium, Low) provides nuanced qualification options. While most users delete low fits immediately, medium fits require strategic decisions. Valley provides detailed reasoning for each score, helping users understand why prospects fall into the medium category.
Common medium-fit scenarios include: right person, wrong company size; right company, junior title; good fit but in a competitive account; partial ICP match with some missing criteria; or strong engagement signals despite weak firmographic fit. These prospects might be worth outreach with adjusted messaging or different campaign strategies.
Best practices for medium fits vary by situation. High-volume teams often include medium fits in campaigns but with different messaging. Resource-constrained teams might exclude them initially, revisiting if high-fit prospects are exhausted. Agencies might present medium fits to clients for manual review. Valley's flexibility allows each team to optimize their approach.
How Can Valley's Scoring Be Customized for Different Industries?
Valley's scoring system is infinitely customizable through natural language ICP definitions. Different industries require different qualification criteria, and Valley adapts accordingly. A cybersecurity company might prioritize compliance requirements and security maturity. A marketing agency might focus on content production and campaign sophistication. A dev tool company might emphasize technical stack and engineering team size.
The customization extends beyond basic firmographics. Valley can be trained to recognize industry-specific signals: "Score higher if they mention HIPAA compliance" for healthcare tech, "Prioritize companies using Kubernetes" for cloud infrastructure, or "Focus on businesses with physical locations" for retail tech. These instructions integrate seamlessly into Valley's scoring algorithm.
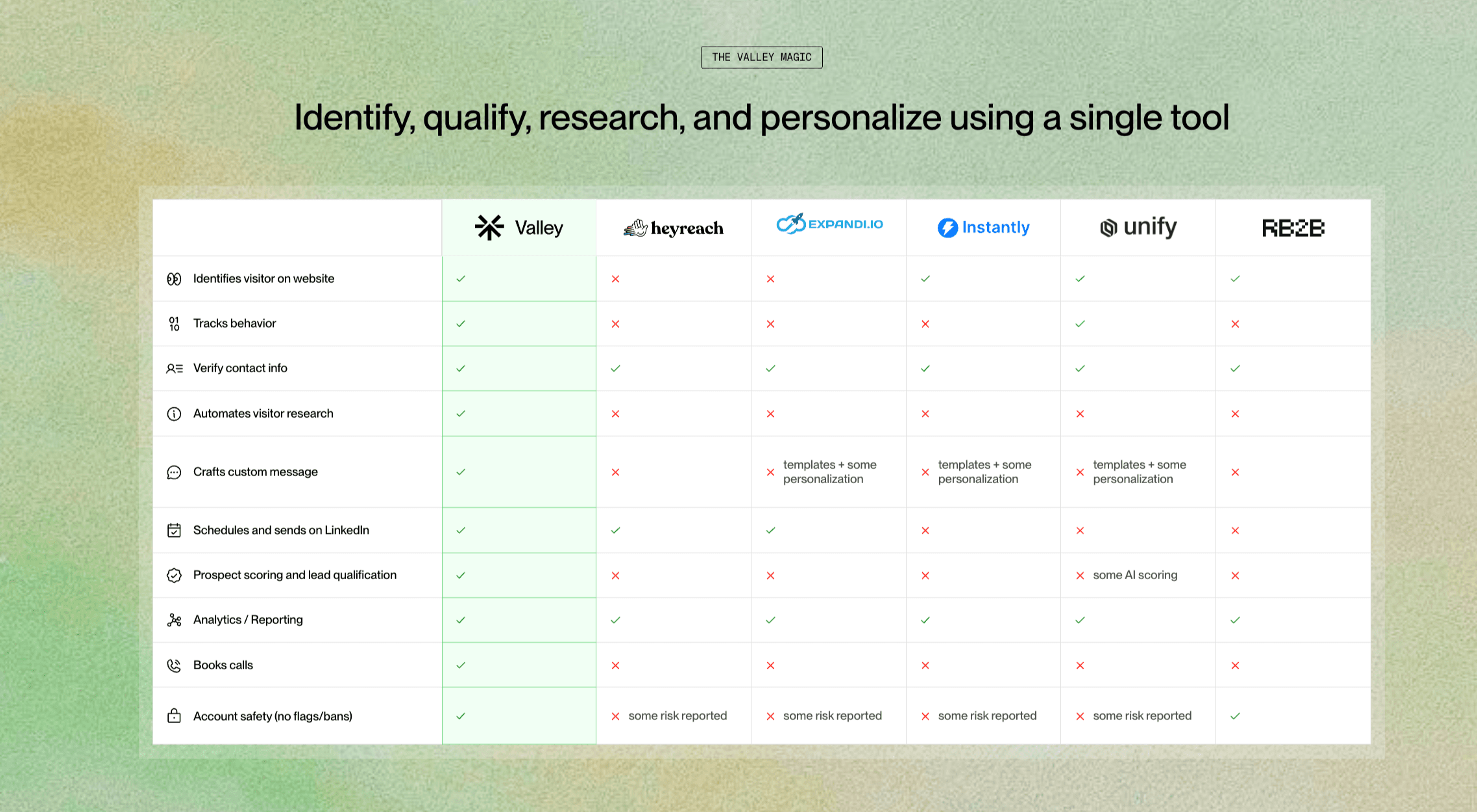
Multiple scoring profiles can exist within one account. Create different products for different market segments, each with unique qualification criteria. Valley applies the appropriate scoring based on campaign configuration, ensuring each prospect is evaluated against relevant criteria. This flexibility enables sophisticated go-to-market strategies across diverse market segments.
VALLEY MAGIC
















