How to Scale LinkedIn Outreach With Valley
Table of contents
Try Valley
Make LinkedIn your Greatest Revenue Channel ↓

Saniya Sood
How Does Valley Enable LinkedIn Outreach Scaling Beyond Manual Capacity?
Manual LinkedIn outreach hits hard capacity limits around 15-20 quality conversations per week per person. Each prospect requires profile research (10-15 minutes), message crafting (5-10 minutes), sending and tracking (2-3 minutes), and follow-up management (5-10 minutes) roughly 25-40 minutes total per prospect.
At this rate, one person maxes out at 15-20 prospects weekly, or 60-80 monthly. For teams needing to engage hundreds or thousands of prospects to hit pipeline targets, manual approaches fail mathematically.
Valley solves the scaling problem through automation of time-intensive research and personalization, intelligent qualification that focuses effort on best-fit prospects only, signal-based targeting that finds prospects already interested, multi-seat orchestration enabling team-level scaling, and consistent execution that maintains quality regardless of volume.
Teams using Valley scale from 60-80 manual monthly outreach to 600-800+ automated monthly engagement per seat; 10x capacity multiplication without additional headcount.
► Book a demo and explore how Valley can support your use case
What Bottlenecks Does Valley Remove From LinkedIn Outreach Scaling?
► Check Out More of Valley's Incredible Outreach: A compilation of real time messages and responses!
Scaling challenges manifest across multiple dimensions. Valley addresses each systematically.
Research Bottleneck: Manual process: Find prospect → Open LinkedIn profile → Review background → Check company website → Google recent news → Synthesize insights (15 minutes per prospect)
Valley automation: Captures signal → Enriches automatically → Researches across 25+ sources → Generates insights → Ready for outreach (30 seconds per prospect)
Time savings: 14.5 minutes per prospect × 500 prospects monthly = 120+ hours saved per seat
Personalization Bottleneck: Manual process: Review research → Identify relevant angle → Craft unique message → Edit for tone → Proofread (10 minutes per prospect)
Valley automation: AI analyzes research → Generates personalized message in your voice → Presents for approval (1 minute review per prospect)
Time savings: 9 minutes per prospect × 500 prospects monthly = 75+ hours saved per seat
Targeting Bottleneck: Manual process: Build prospect lists → Scrape LinkedIn → Validate job titles → Check company fit → Remove duplicates (2-3 hours per 100 prospects)
Valley automation: Monitors signals continuously → Captures only relevant prospects → Qualifies against ICP automatically → Deduplicates across campaigns (zero manual effort)
Time savings: ~10-15 hours monthly per seat
Follow-Up Bottleneck: Manual process: Track who was contacted when → Determine follow-up timing → Craft follow-up messages → Send manually (ongoing management burden)
Valley automation: Sequences execute automatically → Timing optimized by AI → Consistent follow-up without manual tracking
Time savings: 15-20 hours monthly per seat
Combined Impact: Valley eliminates 220+ hours monthly of manual work per seat, freeing sales capacity for high-value activities: responding to interested prospects, conducting discovery calls, delivering demos, negotiating deals, and building relationships.
How to Configure Valley for Multi-Seat Team Scaling?
Individual scaling provides 10x capacity gains. Team-level scaling multiplies those gains across your entire sales organization.
Step 1: Seat Allocation Strategy Determine optimal seat deployment across team:
One seat per SDR (dedicated prospecting capacity) Shared seats for AE team (supplemental prospecting alongside closing) Specialized seats for different ICPs (vertical-specific targeting) Geography-based seats (regional territory coverage)
Most teams start with 3-seat deployment (Valley Growth plan) and expand based on results.
Step 2: Workspace Organization Valley provides workspace management for team coordination:
Create shared ICP definitions all team members reference Establish company-wide DNC lists (competitors, customers, partners) Define standard writing styles and tone guidelines Set up campaign naming conventions for clarity Configure shared exclusion rules
This standardization ensures consistent brand voice and prevents duplicate outreach.
Step 3: Territory and Account Assignment Prevent team members from messaging the same prospects:
Assign geographic territories (East Coast, West Coast, EMEA, etc.) Allocate by industry vertical (FinTech, Healthcare, SaaS, etc.) Distribute by company size (Enterprise, Mid-Market, SMB) Define account ownership (named accounts assigned to specific reps)
Valley's deduplication checks prevent cross-territory conflicts when configured properly.
Step 4: Campaign Coordination Coordinate campaign types across team:
Profile viewer campaigns per rep (each rep's profile viewers go to them) Post engagement campaigns centralized (company posts engagers distributed by territory) Website visitor campaigns routed by fit (high-value accounts to AEs, standard to SDRs) Competitor content campaigns assigned by competitive positioning expertise
Step 5: Response Routing Configure how Valley routes prospect responses:
Direct responses to seat owner for their campaigns Hot leads from high-value accounts escalated to senior reps immediately Tier-based routing (best-fit to AEs, okay-fit to SDRs) Calendar link customization per team member
Step 6: Performance Tracking Monitor team-level and individual metrics:
Outreach volume by seat Response rates by team member Meeting booking rates by seat Pipeline contribution by rep Message quality scores (approval rate, edit frequency)
This visibility enables coaching and optimization across the team.
How Does Valley Maintain Quality While Scaling Volume?
The scaling challenge isn't just volume—it's maintaining personalization quality and relevance as volume increases. Valley preserves quality through systematic quality controls.
AI Training Per Seat: Each team member trains their own Valley AI instance during the 30-day onboarding:
Individual writing style learning Personal tone and voice replication Role-specific value proposition emphasis Different messaging approaches by rep
This individual training ensures messages from each seat sound like that specific rep, not generic automation.
Approval Workflows: Valley provides configurable approval requirements:
Full manual approval for first 30 days (quality training period) Selective approval for Tier 1 prospects after training (high-value accounts reviewed) Autopilot for Tier 2-3 prospects (AI generates and sends after confidence threshold met)
Teams can tighten or loosen approval requirements based on comfort and AI performance.
Quality Scoring: Valley scores message quality automatically:
Personalization depth (how specific are references?) Research accuracy (do facts align with prospect reality?) Tone alignment (does message match trained voice?) Relevance score (does message address prospect's likely interests?)
Low-scoring messages flag for review before sending.
Response Quality Monitoring: Track prospect response sentiment:
Positive responses (interested, wants to talk) Neutral responses (acknowledging but not committing) Negative responses (not interested, remove from list) Angry responses (upset by outreach approach)
High negative/angry response rates signal quality issues requiring immediate intervention.
Regular Quality Audits: Conduct periodic message reviews:
Sample 20-30 messages monthly per seat Evaluate personalization quality independently Identify drift from desired voice Provide corrective feedback to AI
These audits catch quality degradation before it impacts results significantly.
Prospect Feedback Integration: When prospects provide feedback (positive or negative), incorporate into training:
"Your message was very personalized—appreciated the research" → reinforce approach "This seemed automated—too generic" → tighten personalization requirements "Wrong assumptions about my role" → improve research accuracy
Prospect feedback provides ground truth on quality perception.
How to Scale LinkedIn Outreach Across Multiple ICPs?
Most B2B companies serve multiple customer segments. Valley enables ICP-specific scaling without operational complexity.
Multi-Product Configuration: Create separate "Products" in Valley for each ICP:
Product 1: SMB SaaS companies (sales leaders, 10-100 employees) Product 2: Mid-market B2B services (operations leaders, 100-500 employees) Product 3: Enterprise manufacturing (procurement leaders, 500+ employees)
Each product maintains independent ICP criteria, value propositions, messaging frameworks, and proof points.
ICP-Specific Campaigns: Launch dedicated campaigns per ICP:
Separate profile viewer campaigns for each ICP (different messaging for different segments) Post engagement campaigns targeting ICP-relevant content Website visitor campaigns with ICP-specific routing Competitor campaigns by ICP (different competitors matter to different segments)
Specialized Messaging by ICP: Valley's AI generates ICP-appropriate messaging:
SMB messaging emphasizes speed, simplicity, cost-efficiency Mid-market messaging balances sophistication and accessibility Enterprise messaging focuses on scalability, security, compliance
Configure these preferences per product for automatic adaptation.
Seat Specialization by ICP: Assign team members to specific ICPs:
Rep A owns enterprise ICP campaigns Rep B owns mid-market ICP campaigns Rep C owns SMB ICP campaigns
This specialization builds ICP expertise and improves conversion through deeper segment understanding.
Performance Tracking by ICP: Measure results independently per segment:
Response rates by ICP Meeting booking rates by ICP Deal close rates by ICP CAC and LTV by ICP
This analysis reveals which ICPs deliver best ROI and deserve increased investment.
Dynamic ICP Expansion: As certain ICPs prove successful, scale them aggressively:
Increase seat allocation to high-performing ICPs Reduce investment in underperforming segments Test adjacent ICPs that share characteristics with winners
Valley's multi-product architecture enables this dynamic optimization.
What Team Structures Work Best for Valley LinkedIn Scaling?
Organizational design determines scaling effectiveness. Different team structures suit different company stages and strategies.
SDR-Led Model: Dedicated SDRs own Valley seats for pure prospecting:
Each SDR manages 1-2 Valley seats Full-time focus on LinkedIn outbound plus other channels Pass qualified meetings to AE team Measured on meeting volume and quality
Best for: Companies with dedicated SDR function, high-velocity sales models
AE-Led Model: Account Executives use Valley for their own prospecting:
Each AE has 1 Valley seat for territory prospecting Combines prospecting with deal progression Books own meetings and follows through to close Measured on pipeline generation and closed revenue
Best for: Field sales organizations, relationship-driven sales, smaller teams
Hybrid Model: SDRs and AEs both use Valley for different purposes:
SDRs use Valley for cold outbound to new accounts AEs use Valley for account expansion and warm introduction to existing customer accounts Specialized roles for different stages of customer journey
Best for: Companies with complex sales processes, large deal sizes
Agency Model: Agencies use Valley to deliver LinkedIn outreach as a service:
One seat per client or shared seats across multiple clients Agency team manages campaigns on behalf of clients Results reporting to demonstrate ROI Measured on client results and retention
Best for: Marketing agencies, lead gen agencies, fractional sales teams
RevOps-Led Model: Revenue Operations owns Valley for centralized campaign execution:
RevOps team configures all campaigns and ICP definitions Sales team provides input but doesn't manage platform directly Ensures consistent execution and high-quality data Measured on pipeline contribution and process efficiency
Best for: Data-driven organizations, companies prioritizing consistency, teams with strong RevOps function
Each structure scales differently choose based on your sales methodology and organizational capabilities.
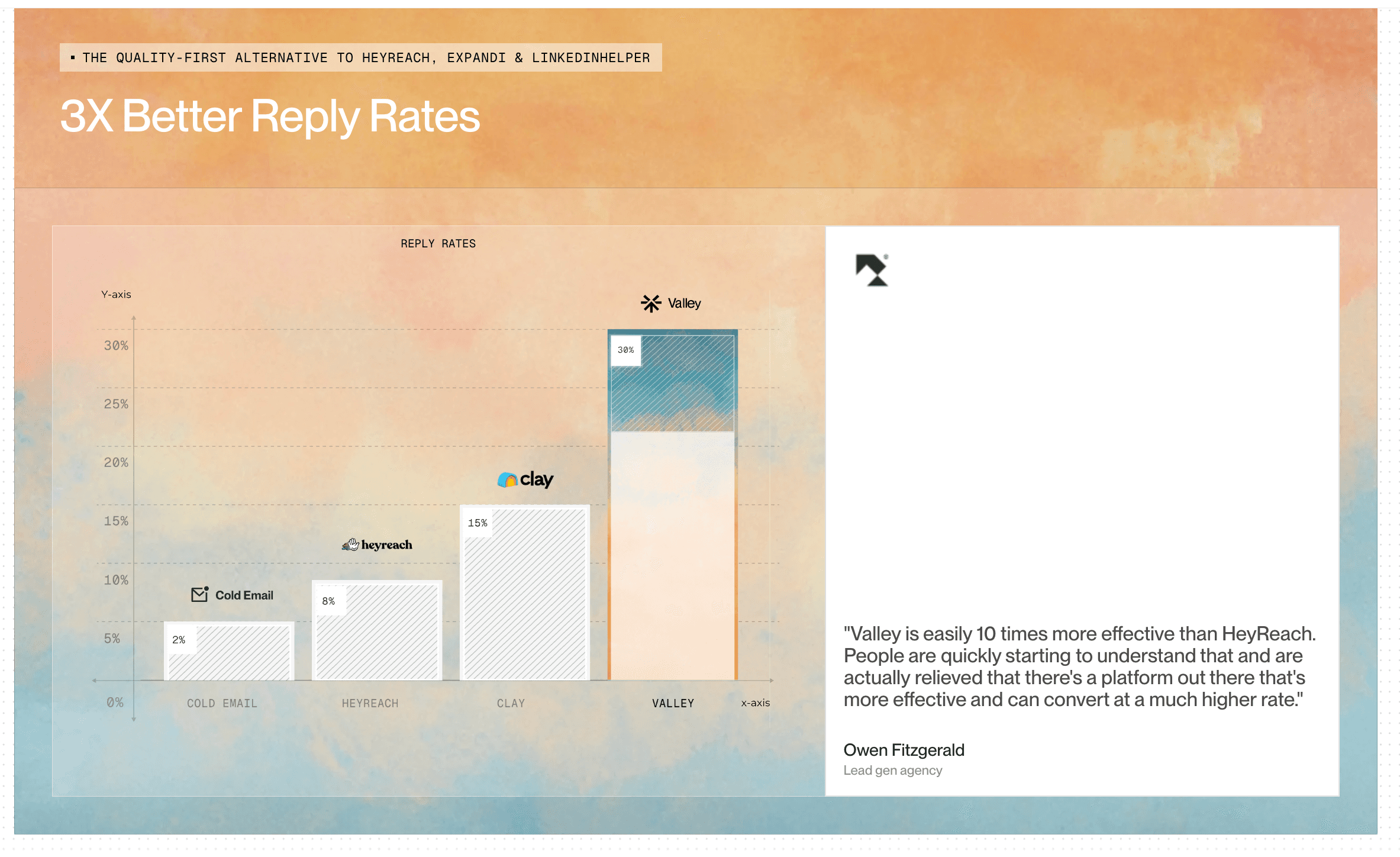
How to Measure Valley's Impact on LinkedIn Outreach Scaling?
Scaling success requires measurement across volume, efficiency, and outcomes.
Volume Metrics: Track raw capacity increases:
Monthly outreach volume before Valley vs. after Prospects engaged per seat per month Total LinkedIn conversations initiated Follow-up message volume
Target: 10x increase in monthly outreach volume per seat
Efficiency Metrics: Measure time savings and productivity:
Hours saved on research and personalization per month Percentage of time reallocated to high-value activities (calls, demos) Cost per outreach attempt (fully loaded including tool and labor) Time from signal capture to first message
Target: 15+ hours saved per seat per month
Quality Metrics: Ensure scaling doesn't sacrifice outcomes:
Response rate comparison (manual vs. Valley) Meeting booking rate Pipeline quality (close rate from Valley-sourced meetings) Customer satisfaction with Valley-generated messaging
Target: Maintain or exceed manual outreach response rates
Business Impact Metrics: Connect scaling to revenue outcomes:
Pipeline generated from Valley campaigns Revenue influenced by LinkedIn outreach CAC for Valley-sourced customers vs. other channels LTV of customers from LinkedIn vs. other sources
Target: Valley-sourced pipeline covers tool cost by 10-20x
Team Scaling Metrics: Measure organizational capacity growth:
Revenue per sales headcount (increasing as Valley multiplies capacity) Pipeline per SDR (should increase significantly) AE productivity (more time closing, less time prospecting) Time to quota attainment for new reps (faster with Valley support)
Target: Defer headcount expansion 6-12 months through Valley scaling
These metrics demonstrate Valley's scaling impact quantitatively, justifying investment and informing expansion decisions.
VALLEY MAGIC
















